🎨 Creating your own UI
If CameraAwesomeBuilder.awesome() doesn't fit your needs in terms of layout, you can create your own UI using the CameraAwesomeBuilder.custom() constructor.
The camera preview will be visible behind what you will provide to this builder.
CameraAwesomeBuilder.custom(
saveConfig: SaveConfig.photoAndVideo(),
builder: (cameraState, preview) {
// Return your UI (a Widget)
return cameraState.when(
onPreparingCamera: (state) => const Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator()),
onPhotoMode: (state) => TakePhotoUI(state),
onVideoMode: (state) => RecordVideoUI(state, recording: false),
onVideoRecordingMode: (state) => RecordVideoUI(state, recording: true),
);
},
)
You can find more examples on the example folder.
Properties
| Method | Comment |
|---|---|
| aspectRatio | Initial aspect ratio of photos and videos taken |
| builder | Create your own interface using the builder method. |
| enablePhysicalButton | When set to true, volume buttons will capture pictures/videos depending on the current mode. |
| filter | Initial preview filter which will be applied to the photo |
| imageAnalysisConfig | Image format, resolution and autoStart (start analysis immediately or later) |
| onImageForAnalysis | Callback that will provide an image stream for AI analysis |
| onPreviewTapBuilder | Customize the behavior when the camera preview is tapped (tap to focus by default) |
| onPreviewScaleBuilder | Customize what to do when the user makes a pinch (pinch to zoom by default) |
| previewAlignment | Alignment of the preview |
| previewFit | One of fitWidth, fitHeight, contain, cover |
| previewPadding | Padding around the preview |
| progressIndicator | Widget to show when loading |
| saveConfig | Define if you want to take photos, videos or both and where to save them. You can also set exif preferences, decide to mirror or not front camera outputs and set video recording settings. |
| sensorConfig | The initial sensor configuration: aspect ratio, flash mode, which sensor to use and initial zoom. |
| theme | Theme used to customize the built-in UI |
Builder method
The builder method is the main method here.
typedef CameraLayoutBuilder = Widget Function(CameraState cameraModeState, PreviewSize previewSize, Rect previewRect);
CamerAwesome works using a state pattern to make sure you can only call methods available on the current camera state. The magic is that you don't have to do anything apart calling some methods using the camera state.
state.when(
onAnalysisOnlyMode: (analysisCameraState) => analysisCameraState.startAnalysis(),
onPhotoMode: (photoCameraState) => photoCameraState.takePhoto(),
onVideoMode: (videoCameraState) => videoCameraState.startRecording(),
onVideoRecordingMode: (videoRecordingCameraState) => videoRecordingCameraState.stopRecording(),
onPreparingCamera: (preparingCameraState) => Loader(),
onPreviewMode: (previewCameraState) => previewModeState.focus(),
);
previewSize and previewRect are additional parameters that might be used to position your UI around or on top of the camera preview.
CamerAwesome has 6 different states
- PreparingCameraState : camera is starting
- PhotoCameraState : camera is ready to take a photo
- VideoCameraState : camera is ready to take a video
- VideoRecordingCameraState : camera is taking a video
- PreviewCameraState : camera is in preview only mode
- AnalysisCameraState : camera is in analysis only mode
Here is a schema showing the interactions between states:
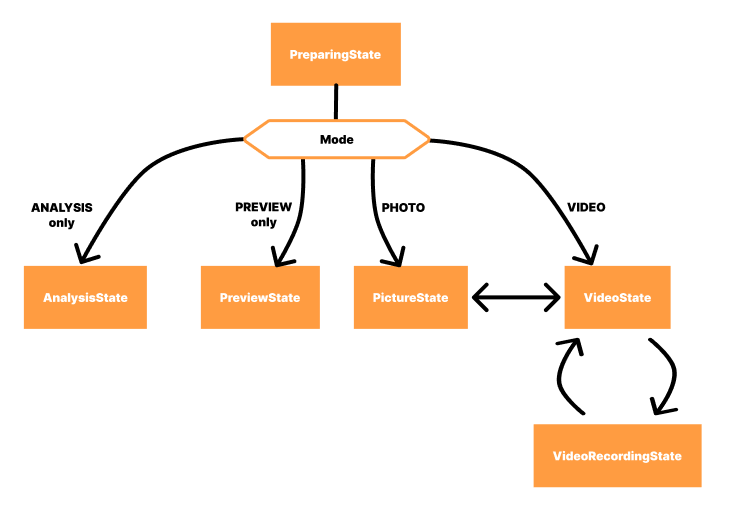
As you can see, after the initial PreparingCameraState, the new state is either PhotoCameraState or VideoCameraState.
A VideoRecordingCameraState replaces the VideoCameraState when a recording starts. You can't start two recording at the same time thanks to this.
When the recording stops, a VideoCameraState replaces it again.
You don't have to worry about state management here
CameraAwesomeBuilder calls the builder method each time you switch between camera states.
This way, you can react to these changes easily in your builder 👌
Creating my own widget
CameraState lets you build a reactive UI by providing you streams and setters to the various properties around the camera.
It should let you create everything you need in a reactive way without worrying about the camera flow.
You can get inspiration on how we built every widgets.
Example
class AwesomeFlashButton extends StatelessWidget {
final CameraState state;
const AwesomeFlashButton({
super.key,
required this.state,
});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return StreamBuilder<SensorConfig>(
// Listen to the current SensorConfig. It might change when switching between front and back cameras.
stream: state.sensorConfig$,
builder: (_, sensorConfigSnapshot) {
if (!sensorConfigSnapshot.hasData) {
return const SizedBox.shrink();
}
final sensorConfig = sensorConfigSnapshot.requireData;
return StreamBuilder<FlashMode>(
// Listen to the currently selected flash mode
stream: sensorConfig.flashMode$,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (!snapshot.hasData) {
return Container();
}
return _FlashButton.from(
// Build your button differently based on the current Flash mode, with different icons for instance
flashMode: snapshot.requireData,
onTap: () => sensorConfig.switchCameraFlash(),
);
},
);
},
);
}
}
In the snippet above, the widget first listens to CameraState.sensorConfig$ to get the most up-to-date SensorConfig. It might change when switching between back and front camera for instance.
Once you have your SensorConfig, you can listen to their properties like the flash mode.
Since we want to listen to its changes, we use flashMode$, which is a Stream of the current flash mode.
👌 Every getter terminated with the $ are streams in CamerAwesome.
The equivalent without $ is the current value. You should not store these in variables since they may change over time.
Using provided widgets
You can find common widgets that you may want to use in the Widgets section.
Many of them use the AwesomeTheme provided to CameraAwesomeBuilder.
Feel free to customize it and reuse this theme in your own UI.
See the theme section for more details.
Instead of handling it yourself, using the built-in widgets can let you rotate your buttons automatically when the phone rotates with AwesomeOrientedWidget for instance.
Check also built-in buttons and the camera mode selector.
Setting and reading camera properties
If you need more customization, you can find details on how to access and update the properties of the camera below.
Note that we recommend to access properties via their Stream whenever possible.
If you need it to build your UI, just use it with a StreamBuilder.
Camera sensor properties and methods
CameraState gives access to the current SensorConfig (via a Stream or a getter).
You will use this object to get or set different sensor related properties.
See the tables below for each use case.
Flash
| Use case | Code |
|---|---|
| Switch between different flash modes | state.sensorConfig.switchCameraFlash() |
| Set a specific flash mode | state.sensorConfig.setFlashMode() |
| Get current flash mode | state.sensorConfig.flashMode |
| Stream of the current flash mode | state.sensorConfig.flashMode$ |
Aspect ratio
| Use case | Code |
|---|---|
| Switch between different aspect ratio | state.sensorConfig.switchCameraRatio() |
| Set a specific aspect ratio | state.sensorConfig.setAspectRatio() |
| Get current aspect ratio | state.sensorConfig.aspectRatio |
| Stream of the current aspect ratio | state.sensorConfig.aspectRatio$ |
Zoom
| Use case | Code | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Set a specific zoom value | state.sensorConfig.setZoom() | Zoom value must be between 0.0 (no zoom) and 1.0 (max zoom) |
| Get current zoom value | state.sensorConfig.zoom | |
| Stream of the current zoom value | state.sensorConfig.zoom$ |
Brightness
| Use case | Code |
|---|---|
| Set a specific brightness | state.sensorConfig.setBrightness() |
| Get current brightness value | state.sensorConfig.brightness |
| Stream of the current brightness value | state.sensorConfig.brightness$ |
Methods and properties available to any CameraState
If you want to access more than just the current SensorConfig, you can explore what the different CameraStates provide.
First of all, they all give you the following features:
| Use case | Code |
|---|---|
| Switch between FRONT and BACK camera | state.switchCameraSensor() |
| Get current Sensor configuration | state.sensorConfig |
| Stream of current Sensor configuration | state.sensorConfig$ |
| Get original SaveConfig | state.saveConfig |
More features are available depending on which CameraState is in use.
PhotoCameraState properties and methods
Take a photo
| Use case | Code |
|---|---|
| Take a photo | state.takePhoto() |
Toggle to save (or not) the location when taking photos
| Use case | Code |
|---|---|
| Set saveGpsLocation | state.saveGpsLocation = true |
| Get saveGpsLocation | state.saveGpsLocation |
| Stream of saveGpsLocation | state.saveGpsLocation$ |
VideoCameraState properties and methods
In this state, you didn't start recording yet.
| Use case | Code | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Start recording a video | state.startRecording() | This will push a VideoRecordingCameraState |
| Enable/Disable audio recording | state.enableAudio() | Must be set before starting a recording. Once started, it can't be changed for the current recording. |
VideoRecordingCameraState properties and methods
In this state, the video recording has started.
| Use case | Code | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Pause a recording | state.pauseRecording() | A paused recording must not be paused again |
| Resume a recording | state.resumeRecording() | A recording not paused should not call resumeRecording() |
| Stop a recording | state.stopRecording() | This will push a VideoCameraState |